티스토리 뷰
1. 문제
https://www.acmicpc.net/problem/2941
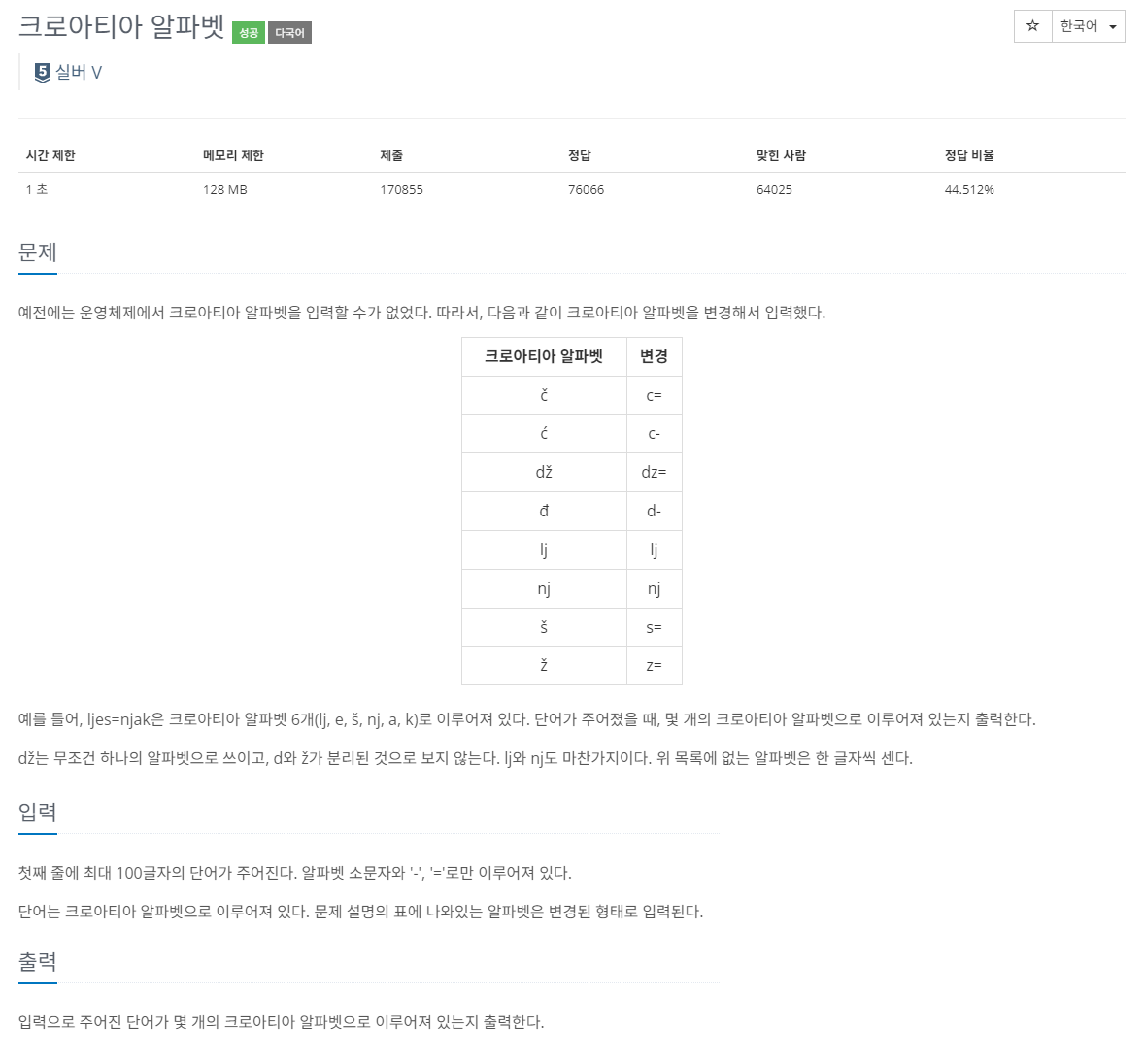
2941번: 크로아티아 알파벳
예전에는 운영체제에서 크로아티아 알파벳을 입력할 수가 없었다. 따라서, 다음과 같이 크로아티아 알파벳을 변경해서 입력했다. 크로아티아 알파벳 변경 č c= ć c- dž dz= đ d- lj lj nj nj š s= ž z=
www.acmicpc.net
2941번 크로아티아 알파벳
2. 해결방안
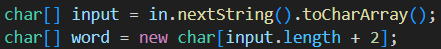
우선, 문자열을 입력받은 후 input변수명을 가진 char[] 배열로 변환시키겠습니다.
그러고나서 다시 word변수명을 가진 char[] 배열에다가 복사를 시킵니다.
이 때, word배열길이는 input배열길이보다 2만큼 길게합니다.
이렇게 배열길이를 잡은 이유는 이따가 언급을 하겠습니다.
크로아티아 알파벳은
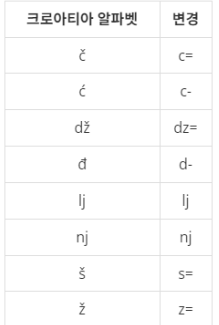
위에서 보이는 표처럼 알파벳 여러개가 한 묶음인것들이 있습니다.
예를들어 dz=lj 가 주어졌다면, dz=와 lj 이렇게 2개로 나누어질 수 있겠습니다.
※ 하지만 여기서 주의할점! ※
위의 표에서 보이는 알파벳을 제외한 abcdefg... 등과 같은 알파벳도 크로아티아 알파벳으로 치기 때문에
예를들어 ac=가 주어졌으면 a도 크로아티아 알파벳으로 봐서 총 2개로 이루어지게 됩니다.
이런 탐색을 거쳤으니 이제 구현만 하면 됩니다.
word배열을 첨부터 길이 - 3만큼까지 순회하면서 조건문 분기로 크로아티아 알파벳을 카운팅합니다.
순회를 길이 - 3까지 한 이유는

위와 같이 단어가 주어졌다고 했을 때 마지막 'd' 인 알파벳을 순회 하게되면
d위치보다 1더 증가한 위치, d위치보다 2더 증가한 위치를 검사해야하기 때문에
word배열을 input배열길이보다 2만큼 더 길게, 순회를 word배열길이보다 3작게 순회를 한 것입니다. (인덱스 초과 방지!)
그렇게 해서 정리하면 다음과 같은 코드를 작성할 수 있습니다.
3. 풀이
/**
* Written by 0xc0de1dea
* Email : 0xc0de1dea@gmail.com
*/
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
//System.setIn(new java.io.FileInputStream("input.in"));
Reader in = new Reader();
char[] input = in.nextString().toCharArray();
char[] word = new char[input.length + 2];
int counting = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < input.length; i++){
word[i] = input[i];
}
for (int i = 0; i < word.length - 2; i++){
if (word[i] == 'c' && (word[i + 1] == '=' || word[i + 1] == '-')){
i++;
counting++;
}
else if (word[i] == 'd' && word[i + 1] == 'z' && word[i + 2] == '='){
i += 2;
counting++;
}
else if (word[i] == 'd' && word[i + 1] == '-'){
i++;
counting++;
}
else if (word[i] == 'l' && word[i + 1] == 'j'){
i++;
counting++;
}
else if (word[i] == 'n' && word[i + 1] == 'j'){
i++;
counting++;
}
else if (word[i] == 's' && word[i + 1] == '='){
i++;
counting++;
}
else if (word[i] == 'z' && word[i + 1] == '='){
i++;
counting++;
}
else {
counting++;
}
}
System.out.print(counting);
}
}
class Reader {
final int SIZE = 1 << 13;
byte[] buffer = new byte[SIZE];
int index, size;
String nextString() throws Exception {
StringBuilder sb = new StringBuilder();
byte c;
while ((c = read()) < 32) { if (size < 0) return "endLine"; }
do sb.appendCodePoint(c);
while ((c = read()) >= 32); // SPACE 분리라면 >로, 줄당 분리라면 >=로
return sb.toString();
}
char nextChar() throws Exception {
byte c;
while ((c = read()) < 32); // SPACE 분리라면 <=로, SPACE 무시라면 <로
return (char)c;
}
int nextInt() throws Exception {
int n = 0;
byte c;
boolean isMinus = false;
while ((c = read()) <= 32) { if (size < 0) return -1; }
if (c == 45) { c = read(); isMinus = true; }
do n = (n << 3) + (n << 1) + (c & 15);
while (isNumber(c = read()));
return isMinus ? ~n + 1 : n;
}
long nextLong() throws Exception {
long n = 0;
byte c;
boolean isMinus = false;
while ((c = read()) <= 32);
if (c == 45) { c = read(); isMinus = true; }
do n = (n << 3) + (n << 1) + (c & 15);
while (isNumber(c = read()));
return isMinus ? ~n + 1 : n;
}
double nextDouble() throws Exception {
double n = 0, div = 1;
byte c;
boolean isMinus = false;
while ((c = read()) <= 32) { if (size < 0) return -12345; }
if (c == 45) { c = read(); isMinus = true; }
else if (c == 46) { c = read(); }
do n = (n * 10) + (c & 15);
while (isNumber(c = read()));
if (c == 46) { while (isNumber(c = read())){ n += (c - 48) / (div *= 10); }}
return isMinus ? -n : n;
}
boolean isNumber(byte c) {
return 47 < c && c < 58;
}
boolean isAlphabet(byte c){
return (64 < c && c < 91) || (96 < c && c < 123);
}
byte read() throws Exception {
if (index == size) {
size = System.in.read(buffer, index = 0, SIZE);
if (size < 0) buffer[0] = -1;
}
return buffer[index++];
}
}